
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are practical tools that may have existed since the mid to late 1900s but only took to popularity in the 2000s; quite realistically, in the past few years. Gaming, film, healthcare, retail, and manufacturing industries have been a driving force behind their popularity. Today, these technologies are reshaping how gamified apps are designed, built, and experienced.
When you combine AR & VR with motivation design mechanics like points, levels, and social rewards, the outcome is a new breed of interactive applications that blur the boundaries between play, learning, and real-world engagement.
In this blog post, we explore how these two technologies transform gamified app development from both developer and user perspectives, outlining technical and design implications, offering the best practices, and proposing a practical roadmap and KPIs to measure success.
Why AR/VR + Gamification Is a Powerful Combo
At their core, gamification does not do anything out of the blue but cleverly leverages human motivators like competition, mastery, social approval, and rewards to change behavior. AR and VR add layers of presence, context, and sensory feedback that amplify those motivations:
Presence & Immersion: VR places users inside a fully controlled experience; AR overlays gameplay onto the real world. Both increase emotional engagement and attention span, which are key drivers of behavior change.
Contextual Interaction: AR ties game mechanics to physical places and objects (location-based quests, object scanning), making rewards feel more relevant and immediate.
Embodies Feedback: Motion, haptic signals, spatial audio and 3D visuals let users feel progress, not just see it in a leaderboard.
Novelty & Virality: New formats create shareable moments and social buzz, and people showing off immersive achievements.
Result: higher retention, deeper learning, higher conversion for commercial apps (e.g., retail, fitness), and stronger habit formation.
How AR/VR Change the User Experience of Gamified Apps
Spatial & Physical Gameplay
Instead of tapping buttons, users move, look around, and manipulate objects. This converts abstract tasks into embodied activities; e.g., a language app where you “walk” through a virtual market and barter, or a fitness app where daily steps become treasure hunts.
Multisensory Feedback
Our gamification solutions involve 3D visuals, spatial audio, and haptics that provide richer rewards. A correct action might trigger a satisfying spatial sound, fireworks in 3D, or a haptic pulse, all of which are stronger reinforcement than a flat badge.
Real-World Blending (AR)
AR anchors digital goals in the environment: point your phone to scan a product to get a coupon, or complete scavenger hunts across the city. The real world becomes a game board, increasing perceived relevance.
Deep Personalization
AR/VR can adapt the environment to the user: scale difficulty based on physical ability, change virtual opponents based on skill, or personalize storylines to past behavior.
Social & Co-Located Experiences
Shared AR experiences (e.g., collaborative AR puzzles) and social VR spaces let players cooperate or compete in presence, boosting social motivation and virality.
How AR/VR Change the Developer Experience
New Design Primitives
Developers shift from 2D UI flows and screens to spatial design: world-building, object affordables, spatial audio mapping, and motion-space flows. UX design becomes environment design.
Different Technical Stack
You’ll commonly use:
- Game engines (Unity, Unreal) for real-time 3D
- AR SDKs (ARKit, ARCore, Vuforia)
- VR SDKs and platforms (OpenXR, Oculus SDK, SteamVR)
- 3D model formats and asset pipelines (gITF, FBX)
- Spatial mapping and persistent anchors for AR
- Networks for multi-user experiences
Performance & Constraints
Real-time 3D demands high performance and low latency. For mobile AR, battery, thermal throttling, and CPU/GPU limits are major constraints. VR demands consistent 90+ FPS for comfortable presence.
New QA & Testing Paradigms
Testers must verify interactions in physical space, across devices, and with varied lighting/real-world conditions. Automated testing is harder; user testing in context is essential.
Interdisciplinary Teams
Successful gamified apps require game designers, 3D artists, sound designers, UX researchers, and systems engineers, and not just app developers.
Common Use Cases Across Industries
Education & Training: Simulated labs, historical reconstructions, or AR overlays in classrooms turn learning tasks into quests and experiments.
Fitness & Wellness: VR workouts (boxing, rhythm games) and AR outdoor challenges gamify exercise with goals, maps, and social competitions.
Retail & Commerce: AR try-ons, scavenger coupon hunts, and VR showrooms gamify discovery and reduce friction in purchase decisions.
Healthcare & Therapy: VR exposure therapy or gamified rehab exercises that track motion and reward progress.
Tourism & Museums: AR tours with location-based challenges and narrative rewards, VR restores inaccessible sites as gamified exploration.
Workplace Upskilling: Simulated scenarios that reward correct procedures, provide instant feedback, and log certification progress.
Design Patterns & Mechanics for AR/VR Gamified Apps
1. Spatial Quests
Define objectives anchored to locations or objects. Use persistent anchors so users can leave and return to progress.
2. Embodied Challenges
Translate tasks into physical movement (e.g., reach, rotate, step). Measure accuracy and reward precision.
3. Environmental Rewards
Reward users with environmental changes: unlock a virtual fountain, change weather, or transform the scene to show achievement.
4. Social Presence & Avatars
Use real-time voice spatialization and avatars to create group tasks or competitions. Allow spectatorship: AR spectators can watch through mobile devices.
5. Adaptive Difficulty via Telemetry
Use motion, success rates, and time-on-task to adapt challenge difficulty and suggested rewards.
6. Collectibles & Persistent Worlds
Let users collect items placed in physical or virtual space. Use cloud anchors to make collectibles visible across sessions and devices.
These patterns illustrate why gamification solutions are evolving rapidly with AR/VR, offering more immersive, meaningful engagement loops.
Technical Considerations & Best Practices
-
Optimize Performance Early
Design low-poly assets, implement level-of-detail (LOD), use texture atlases, and test on the lowest target device. Frame-rate drops break presence.
-
Prioritize Comfort & Motion Design
Avoid mismatched motion cues. For VR, prevent vection-induced motion sickness by minimizing artificial locomotion; prefer teleportation or natural walking in tracked spaces.
-
Use Accessible Input Models
Support different location and interaction options: controllers, hand tracking, gaze, or simple tap-to-place mechanics to include a wider audience.
-
Handle Real-World Variability (AR)
AR must robustly handle lighting changes, occlusion, and varied surfaces. Use fallback UIs when spatial tracking fails and surface detection is ambiguous.
-
Data Privacy & Safety
AR interacts with the environment and often collects location data and camera feeds. Be explicit about data usage, obtain consent, and minimize sensitive data collection.
-
Persistence & Cross-Session Consistency
Use cloud anchors or server-side persistence for AR anchors and user progress so experiences remain consistent across devices.
-
Test In-Context
Lab testing is insufficient. Test in real lighting conditions, varied spaces, and with users of different heights, mobility, and cultural backgrounds.
Monetization Strategies for AR/VR Gamified Apps
- Freemium Progression: Base game free, premium levels, items, or quests paid.
- Cosmetic Purchases: Avatars, virtual clothing, or scene themes.
- Sponsored AR Content: Branded anchors or location-based promotions (e.g., AR coupons at partner stores).
- Data-Driven Upsells: Personalized premium coaching based on telemetry (fitness, edu).
- Sponsorship & Experiential Events: Limited-time branded events in AR/VR spaces.
Be cautious: monetization in immersive spaces can feel intrusive if mismatched with user experience.
KPIs to Measure Success
Retention (D1, D7, D30): Does immersion translate to repeated visits?
Session length & frequency: Are users spending more time per session? Are sessions frequent?
Onboarding completion rate: Are users learning interactions quickly?
Task completion rate & error rate: Are in-world goals understandable and achievable?
Physical engagement metrics: Steps, movement accuracy, completion of embodied tasks.
Social engagement: Number of co-op sessions, invites, or shared moments.
Monetization metrics: Conversion rate to premium, average revenue per user (ARPU).
Comfort complaints/VR sickness reports: Critical for product viability.
Accessibility, Ethics, and Safety
Accessibility: Offer seated options, adjustable difficulty, and text/audio alternatives. Include captions and high-contrast modes for AR overlays.
Physical safety: Warn users about real-world hazards. For AR apps that require motion, include safety prompts and boundary systems.
Privacy: Secure camera feeds, location data, and biometric motion traces. Prefer on-device processing for sensitive data when possible.
Ethics in persuasive design: Gamification can manipulate; design for user benefit and transparency. Avoid exploitative reward loops.
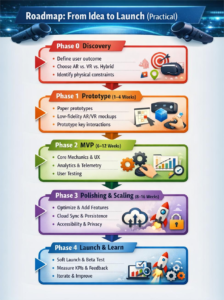
Roadmap: From Idea to Launch (Practical)
Phase 0 — Discovery
- Define core user outcome (learn, move more, shop).
- Choose AR vs. VR vs. hybrid based on use case and target device.
- Identify physical constraints (indoor/outdoor, large spaces, mobility requirements).
Phase 1 — Prototype (1–4 weeks)
- Build a paper prototype for spatial flows.
- Create low-fidelity VR/AR mockups in the engine (Unity/Unreal).
- Prototype key interaction (e.g., object grab, teleport, anchor placement).
Phase 2 — MVP (6–12 weeks)
- Implement core mechanics, minimal content, basic UX flows.
- Integrate analytics and telemetry for behavior measurement.
- Conduct iterative user tests in target environments.
Phase 3 — Polishing & Scaling (8–16 weeks)
- Optimize assets, implement adaptive difficulty, add social features.
- Harden persistence, cloud anchors, and cross-device sync.
- Add accessibility options and privacy controls.
Phase 4 — Launch & Learn
- Soft launch in controlled markets or beta testers.
- Measure KPIs, gather qualitative feedback.
- Iterate on onboarding, motion comfort, and monetization elements.
Challenges You’ll Face (and How to Handle Them)
Hardware Fragmentation: Test across devices; design flexible input/graphics that degrade gracefully.
Tracking & Environmental Variability (AR): Provide manual placement fallbacks and robust error states.
Motion Sickness (VR): Design comfort-first locomotion and provide nausea mitigation options.
Team Coordination: Invest in clear asset pipelines, version control for large binary assets, and cross-discipline planning sessions.
User Education: Use progressive onboarding and contextual help (e.g., inline micro-tutorials).
Future Trends to Watch
AR Cloud & Persistent Worlds: Shared, persistent AR annotations and collectibles accessible across devices and sessions.
Cross-Device Continuity: Seamless transitions between phone AR, headset VR, and desktop experiences.
AI-Driven Environments: Dynamic narratives and NPCs that adapt to each user’s learning curve and play style.
Lower Barrier Hardware: Advances in lightweight AR glasses and standalone VR headsets will expand reach.
Haptics & Wearable Feedback: Affordable wearables will deepen embodied feedback loops.
Quick Checklist for Product Teams
- Define the behavioral outcome and why immersion matters.
- Start with the simplest interaction that proves value (one core loop).
- Prototype in the real world early (especially for AR).
- Measure motion, comfort, retention, and task completion.
- Plan for accessibility and privacy from day one.
- Keep art and code pipelines optimized for mobile and low-power devices.
- Use telemetry to tune difficulty and personalization.
What We Think
AR and VR don’t just add flashy visuals to apps; they change the grammar of interaction. The result is a deeper sense of presence, an ability to embed game mechanics into real-world contexts, and new forms of social, embodied engagement. But with great immersion comes new responsibilities: careful motion design, robust privacy practices, and considered monetization. Teams that pair strong product thinking with the right technical approach can create gamified apps that are not only more fun, but more effective.
How We Can Help
Red Apple Technologies specializes in designing and developing cutting-edge AR & VR in gaming and enterprise applications. From conceptualization to deployment, we help businesses transform traditional apps into fully immersive gamified apps. Here’s what we can do for you:
Custom AR/VR Development: Build tailored VR simulations or AR overlays for education, retail, fitness, tourism, and enterprise training.
Gamification Solutions: Design engaging reward systems, adaptive challenges, and interactive environments that boost user engagement and retention.
End-to-End App Development: From UI/UX design and 3D asset creation to integration, optimization, and launch, we ensure a smooth development lifecycle.
Expert Teams: We have interdisciplinary teams of developers, 3D artists, and UX specialists to ensure that AR/VR projects are immersive, performant, and scalable.
Consulting & Strategy: Guidance on device compatibility, monetization strategies, and data-driven personalization.
Whether you want to launch an AR fitness experience, a VR training simulation, or retail apps, hire app developers with the right expertise to bring your immersive ideas to life efficiently and effectively.
To Have A Better Understanding On This Let us Answer The Following Questions
Answer: Clients often want to know which hardware their users need. AR apps typically run on smartphones, tablets, and increasingly AR glasses (like Apple Vision Pro or Nreal). VR apps require headsets such as Oculus Quest, HTC Vive, or standalone VR headsets. Our development teams optimize experiences across multiple devices to maximize reach without compromising performance.
Answer: Development timelines vary based on complexity:
- Simple AR gamified apps: 8–12 weeks
- VR simulations or mixed-reality experiences: 12-24 weeks
- Enterprise-scale apps with multi-user interactions and persistent worlds: 6+ months
Factors influencing duration include 3D asset creation, spatial interaction design, multiplayer features, and iterative testing in real-world environments.
Answer: AR and VR increase presence, interactivity, and immersion, which leads to higher engagement than traditional apps. Users physically interact with environments, experience multisensory rewards, and share achievements socially. Gamified challenges, leaderboards, and real-time feedback in AR/VR amplify motivation and long-term retention.
Answer: Costs depend on the scope, platform, and content complexity:
- Simple AR apps: $15,000–$40,000
- VR experiences with medium complexity: $40,000–$80,000
- Large-scale enterprise AR/VR apps with persistent worlds: $80,000+
Working with Red Apple Technologies helps optimize costs by leveraging reusable assets, pre-built SDKs, and efficient pipelines.
Answer: Yes. AR/VR gamified apps can integrate with CRM, LMS, e-commerce platforms, fitness trackers, and analytics dashboards. This allows businesses to sync user progress, capture performance metrics, and personalize experiences. Get seamless integration solutions to ensure immersive apps that complement existing digital ecosystems.



























 Book an Appointment
Book an Appointment Get Instant Project Estimation
Get Instant Project Estimation WhatsApp Now
WhatsApp Now






 Book An Appointment
Book An Appointment WhatsApp
WhatsApp







